In other words, it’s possible to connect to the internet on an ever-increasing range of devices. Plus, there’s also quite a few different types of services that allow these devices to get online.
People’s choice over the various devices and means of getting online varies according to many factors, including lifestyle (whether they’re at home or out and about), how frequently they need to access the internet (everyday for a number of hours or just occasional use), the types of things they want to use the internet to do (catch up with email or download and watch films and tv programmes), and budget (internet access companies usually charge to use their services).
Let’s unpackage the above in a bit more detail...
The most common devices people use today to get online, include:
- Desktop computers
- Laptop computers
- Mobile phones
- Tablets
- E-readers
However, the range of devices capable of connecting to the internet is ever-expanding and shifting our understanding of what “being online” means.
In recent years, we’ve seen the emergence of smart watches, central heating systems, and even refrigerators, which by connecting to the internet can perform all sorts of enhanced and useful functions.
Still, the most “traditional” devices used for accessing and browsing the internet today are desktop computers, laptop computers, tablets and smartphones.
Two types of internet connection services
There are two key types of service that can provide you with internet access. They are:
- Fixed internet
- Mobile internet
Let's take a look at each, in turn...
As the name suggests, this is an internet connection that is fixed to a specific location (such as a home, office or shop) — meaning that the internet connection is unique to that property, and as such you can only access it when you’re physically situated there.
Today, the three most common types of fixed internet connection are:
ADSL broadband
The most widely used form of internet connection, ADSL uses a property’s existing phoneline to get online.
This form of broadband has been available for a while, making it often the most cost-effective way of getting online — yet not the fastest (average download speeds of 8.4 Mb) compared to the two other available forms of internet connection now available in the UK, cable and fibre broadband.
Cable broadband
Instead of using a phone line as ADSL does, cable broadband establishes an internet connection via a specialised cable that shares the same line as your TV service.
Cable broadband generally offers higher speeds than ADSL connections (average download speeds of 50.5 mb), but as a cable broadband connection is often shared with many other users, speeds can suffer from time to time due to congestion during peak times.
Fibre broadband
The most recently rolled out form of internet connection in the UK (and therefore, still not that widely available) is fibre broadband.
Fibre broadband claims to offer more consistent and reliable speeds than cable and ADSL (average download speeds of 59.4mb) — allowing multiple devices to be performing high-capacity tasks, simultaneously, without any slow downs or breakages in the connection, making it an attractive proposition for busy family homes or office environments.
Choosing a fixed internet service provider
Many companies provide installation of one of the above types of fixed internet connection, with ongoing access to the connection at an agreed speed and data usage offered, mostly on a contract basis.
Some companies are more specialised in one type of connection than another. For instance, Virgin Media specialises in cable broadband connections as it is also a TV service provider. Whilst BT, as the owner of the majority of the UK’s telephone lines, is most well-known for providing ADSL broadband — though many third-party companies are allowed access to BT’s network and offer their own ADSL broadband services. As the owner of the new infrastructure that allows for latest fibre broadband, BT is also currently the sole provider of this next-generation service.
Mobile internet is a way of getting online anywhere without relying on a fixed-location connection — as the name suggests, by using your mobile device.
Mobile phone operators provide access to this alternative method of internet usage. When you sign up to a mobile phone operator’s services — either on a contract or pay-as-you-go basis — you can include access to a certain amount of data (measured in megabytes), allowing you to use your mobile device to connect to the internet within that capped usage limit.
Mobile internet is currently offered at two different speeds and capability levels:
3G mobile internet: has been around for many years and typically offers basic access and download speeds that allow users to complete basic tasks such as load a web page or access an email. 3G mobile internet is gradually being replaced by 4G services.
4G mobile internet: is the more recently available level of mobile internet available, offering much higher speeds than 3G. In fact, due to excellent connection and download speeds, 4G might eventually replace fixed internet connections in more rural parts of the country that may struggle to get access to quicker connections.
5G mobile internet: is the proposed next telecommunications standard beyond the current 4G advanced standards.
In conclusion
So there you have it. Hopefully, this has given you enough awareness and basic knowledge to be able to make your first moves towards getting online, and using the internet. Go for it!


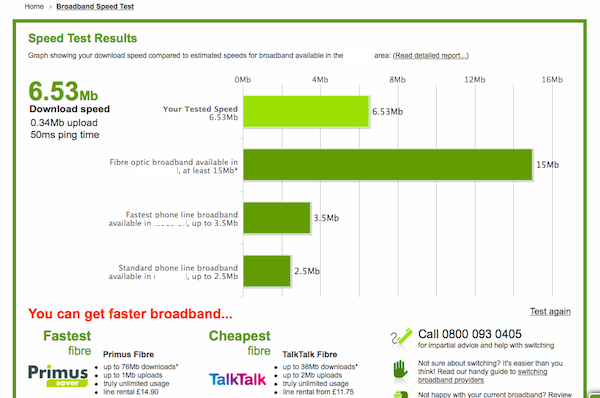

 Step 1: Set up your wireless router - an example of which is on the right - (see How to connect to the internet for instructions). Most internet providers now supply wireless routers as standard. When setting up one, it’s important to provide appropriate security so that your computer can’t be entered by anyone but you. Instructions for this should be supplied with the router, but if in doubt, consult an expert.
Step 1: Set up your wireless router - an example of which is on the right - (see How to connect to the internet for instructions). Most internet providers now supply wireless routers as standard. When setting up one, it’s important to provide appropriate security so that your computer can’t be entered by anyone but you. Instructions for this should be supplied with the router, but if in doubt, consult an expert. Step 2: Check that your computer has a built-in wireless adaptor (see left). Up-to-date laptops generally have one, but most desktop computers don’t.
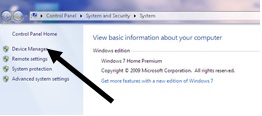
Step 2: Check that your computer has a built-in wireless adaptor (see left). Up-to-date laptops generally have one, but most desktop computers don’t.
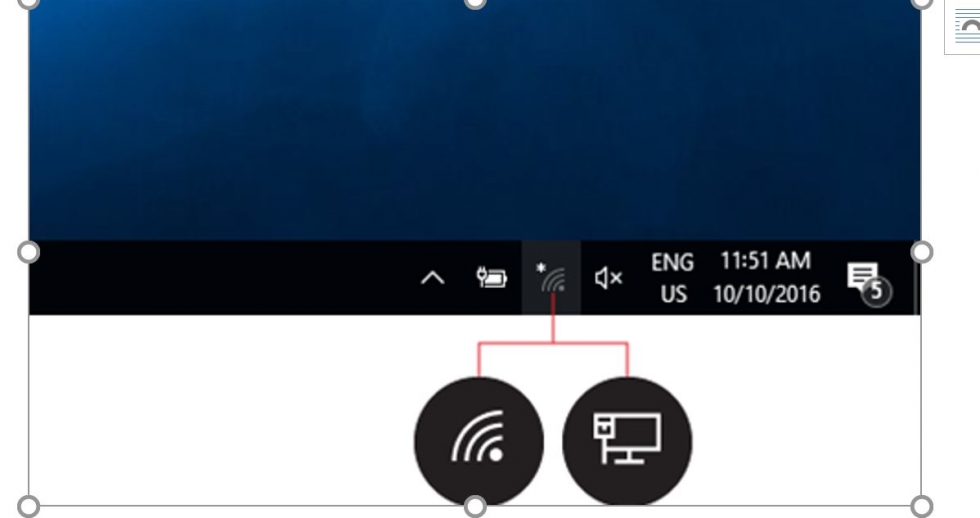
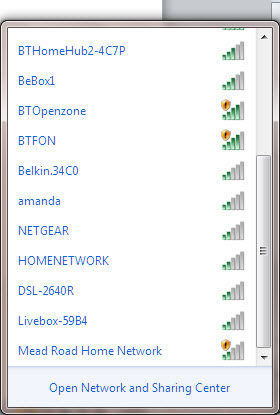 Step 3: To connect to a wireless network, click the wifi icon. You should now see a list of available networks – an example is on the left.
Step 3: To connect to a wireless network, click the wifi icon. You should now see a list of available networks – an example is on the left.